Introduction
Once SAML SSO authentication is complete and an auth code has been generated, the next critical phase begins: Authorization. This comprehensive guide explores how the one-time auth code is securely exchanged for access tokens, how those tokens enable API access control through AWS Lambda authorizers, and how role-based permissions are enforced throughout the system.
Building on the foundation established by our SSO implementation, this authorization system provides fine-grained access control to the SecureFinance Retail Banking Application, ensuring that users can only access the resources and perform the actions appropriate to their roles.
Table of Contents
- Authorization Overview
- Auth Code to Access Token Exchange
- Token Management and Refresh
- Lambda-Based API Authorization
- Request Authorization Flow
- Policy-Based Access Control
- Implementation Deep Dive
- Security Considerations
- Best Practices
- Conclusion
Authorization Overview
The Authorization Challenge
After successful SSO authentication, users possess a one-time auth code that must be converted into usable access tokens. The authorization system must:
- Securely exchange the auth code for access tokens
- Validate and authorize every API request using Lambda functions
- Enforce role-based permissions based on user context
- Manage token lifecycle, including refresh and expiration
- Filter data access based on user relationships and permissions
Three-Layer Security Model
Our authorization implementation follows a comprehensive three-layer approach:
┌─────────────────┬─────────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────┐
│ Authentication │ Authorization │ Data Filtering │
├─────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┤
│ ✅ Complete │ User API guards actions │ Domain services filter │
│ (SSO Flow) │ that users can perform │ data based on user │
│ │ using Lambda authorizers │ context and permissions │
│ │ and Redis policy cache │ │
└─────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴──────────────────────────┘
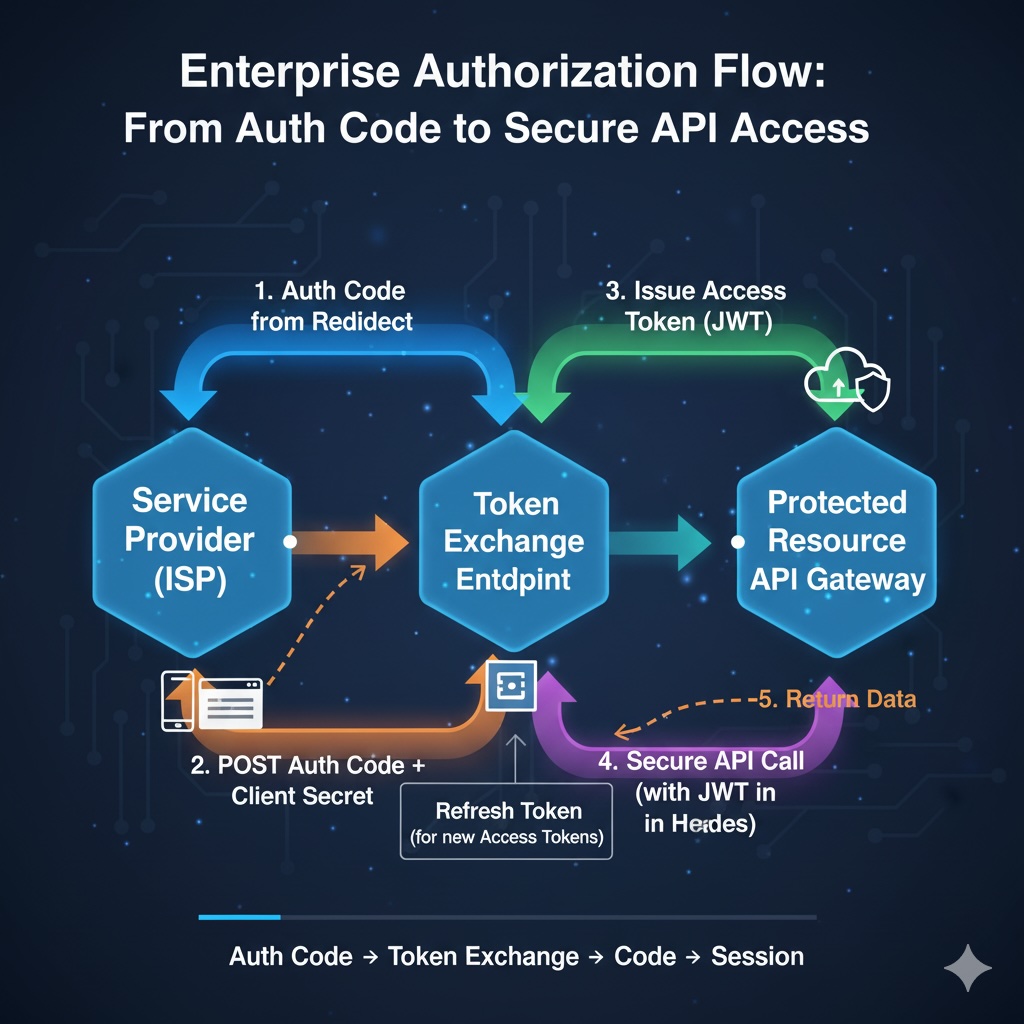
Auth Code to Access Token Exchange
The auth code received from the SSO callback must be exchanged for access tokens that can authenticate API requests.
Token Exchange Architecture
Token Exchange Implementation Details
Auth Code Validation Process:
Access Token Structure
The access token is implemented as a JWT (JSON Web Token) with the following claims:
{
"iss": "securefinance-user-api",
"sub": "user-12345",
"aud": "securefinance-banking-api",
"exp": 1693420800,
"iat": 1693417200,
"role": "personal-banking-customer",
"customer_id": "CUST-98765",
"permissions": [
"accounts:read",
"transactions:read",
"transfers:create"
],
"scope": "banking-services"
}
Token Management and Refresh
Token Lifecycle Management
Access Token Properties:
- Validity: 60 minutes (configurable based on security policies)
- Format: JWT with digital signature
- Scope: Limited to banking services
- Revocation: Can be invalidated immediately if needed
Refresh Token Properties:
- Validity: 30 days (sliding window)
- Format: Secure random string (256-bit)
- Storage: Encrypted in the database
- Single-use: Each refresh generates a new token pair
Token Refresh Flow
Sliding Window Refresh Strategy
Lambda-Based API Authorization
Every API request to banking services must be authorized through AWS Lambda functions that validate tokens and enforce permissions.
Lambda Authorization Architecture
Lambda Authorizer Implementation
Request Authorization Flow
The complete flow from API request to data access involves multiple validation steps and policy evaluations.
Complete Request Authorization Sequence
Policy-Based Access Control
The authorization system uses policy-based access control (PBAC) to determine what actions users can perform.
Permission Matrix
| Role | Resource | Allowed Actions | Data Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| personal-banking-customer | Accounts | read | Own accounts only |
| personal-banking-customer | Transactions | read | Own transactions only |
| personal-banking-customer | Transfers | create, read | Between own accounts |
| business-banking-customer | Business Accounts | read, write | Authorized business accounts |
| business-banking-customer | Payroll | create, read, update | Company payroll only |
| relationship-manager | Customer Accounts | read | Assigned customers only |
| relationship-manager | Reports | create, read | Customer segment reports |
| banking-operations-staff | All Accounts | read, write | Administrative access |
| banking-operations-staff | Audit Logs | read | Full system audit access |
Policy Evaluation Engine
Redis Policy Caching
To optimize performance, authorization policies are cached in Redis with intelligent cache management:
Cache Key Strategy
Cache Key Format: policy:{user_id}:{api_endpoint}:{action}
Examples:
policy:user-12345:accounts:readpolicy:user-67890:transactions:createpolicy:user-11111:reports:generate
Cache Management:
- TTL: 5 minutes for most policies
- Invalidation: When user roles change
- Size: Maximum 10,000 policies per instance
- Eviction: LRU (Least Recently Used)
Implementation Deep Dive
Token Exchange Service Implementation
Lambda Authorizer Code Structure
// Lambda Authorizer Core Logic
export const authorizer = async (event: APIGatewayAuthorizerEvent): Promise<AuthPolicy> => {
try {
// Extract JWT token from Authorization header
const token = extractBearerToken(event.authorizationToken);
// Validate JWT signature and expiration
const claims = await validateJWT(token);
// Build cache key for policy lookup
const cacheKey = buildPolicyCacheKey(claims.sub, event.methodArn);
// Check Redis cache for existing policy
let policy = await policyCache.get(cacheKey);
if (!policy) {
// Cache miss - evaluate permissions
const userPermissions = await getUserPermissions(claims.sub);
const requiredPermissions = getRequiredPermissions(event.methodArn);
policy = evaluatePermissions(userPermissions, requiredPermissions);
// Cache policy for 5 minutes
await policyCache.setex(cacheKey, 300, JSON.stringify(policy));
}
return buildAuthPolicy(claims.sub, policy);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Authorization failed:', error);
return buildDenyPolicy();
}
};
Service-to-Service Authentication
For backend services that need to communicate without a user context:
Security Considerations
Token Security Best Practices
JWT Token Security:
- Use strong signing algorithms (RS256 minimum)
- Keep token payloads minimal to reduce attack surface
- Implement proper key rotation schedules
- Never include sensitive data in JWT claims
Refresh Token Security:
- Store refresh tokens encrypted in database
- Implement token binding to prevent token theft
- Use secure random generation (256-bit minimum)
- Implement suspicious activity detection
Authorization Security Measures
Attack Prevention Strategies
Common Attack Vectors and Mitigations:
- Token Replay Attacks
- Short token lifetimes (60 minutes)
- JTI (JWT ID) claims for uniqueness tracking
- Network-level IP validation
- Permission Escalation
- Strict role-based permission mapping
- Regular permission audits
- Principle of least privilege enforcement
- Cache Poisoning
- Signed cache entries
- TTL limits on cached policies
- Cache invalidation on security events
Best Practices
Authorization Implementation Checklist
Token Management:
- [ ] Implement proper JWT validation with signature verification
- [ ] Use appropriate token lifetimes (60 min access, 30 days refresh)
- [ ] Implement secure refresh token rotation
- [ ] Add comprehensive token audit logging
Lambda Authorization:
- [ ] Cache authorization policies effectively
- [ ] Implement proper error handling and fallback policies
- [ ] Monitor Lambda authorizer performance and errors
- [ ] Use least-privilege IAM roles for Lambda execution
Security Monitoring:
- [ ] Track failed authorization attempts
- [ ] Monitor unusual access patterns
- [ ] Implement automated security incident response
- [ ] Regular security assessment and penetration testing
Performance Optimization
Caching Strategy:
- Use Redis for high-performance policy caching
- Implement intelligent cache warming for frequently accessed resources
- Monitor cache hit rates and adjust TTL values accordingly
Lambda Optimization:
- Keep authorizer Lambda functions warm with provisioned concurrency
- Minimize cold start times by optimizing dependencies
- Use connection pooling for database and cache connections
Conclusion
The authorization flow seamlessly continues from where SSO authentication left off, transforming the one-time auth code into a comprehensive access control system. This implementation provides:
Key Achievements
- Secure Token Exchange: Auth codes are safely converted to JWT access tokens with 60-minute lifetimes and refresh tokens valid for 30 days
- Scalable Authorization: AWS Lambda authorizers provide real-time permission validation with Redis caching for optimal performance
- Fine-Grained Access Control: Role-based permissions ensure users can only access appropriate resources and perform authorized actions
- Robust Security: Multiple layers of validation, encryption, and monitoring protect against common attack vectors
- Audit Compliance: Comprehensive logging and monitoring support regulatory requirements and security analysis
The Complete Flow
From initial SSO authentication through final data access:
- SSO Authentication → Auth code generation (10-minute lifetime)
- Token Exchange → Access token (60 minutes) + Refresh token (30 days)
- API Authorization → Lambda-based permission validation with Redis caching
- Data Filtering → Context-aware resource access based on user roles
- Token Refresh → Seamless token renewal without re-authentication
This authorization system ensures that the SecureFinance Retail Banking Application can serve multiple user types – from individual banking customers to relationship managers and operations staff – while maintaining the highest security standards and optimal user experience.
The combination of SAML SSO for authentication and Lambda-based authorization creates a robust, scalable foundation for secure enterprise applications in the financial services industry.
Auto Amazon Links: No products found.
