Introduction
Single Sign-On (SSO) has become the cornerstone of secure enterprise authentication, enabling users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials. This comprehensive guide explores the implementation of SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) SSO in a real-world financial services scenario where TechCorp acts as an Identity Provider (IdP) for users accessing the SecureFinance Retail Banking Application.
In this detailed technical walkthrough, we’ll examine how the SAML SSO flow works from initial trust setup through successful auth code generation, setting the foundation for subsequent authorization processes.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the SSO Challenge
- SAML SSO Architecture Overview
- Trust Relationship Setup
- SAML SSO Authentication Flow
- Auth Code Generation Process
- Role-Based User Context
- Implementation Deep Dive
- Security Considerations
- Best Practices
- Conclusion
Understanding the SSO Challenge
The Business Scenario
TechCorp, a financial services organization, needs to provide secure access for its clients and employees to the SecureFinance Retail Banking Application. The challenge involves managing different user types:
- Personal Banking Customers: Individual account holders
- Business Banking Customers: Corporate account managers
- Relationship Managers: TechCorp employees serving clients
- Banking Operations Staff: Internal support personnel
Each user type requires seamless access while maintaining strict security controls and audit trails.
The SSO Solution Framework
Our implementation uses SAML 2.0 to establish a trust relationship where:
- TechCorp acts as the Identity Provider (IdP)
- SecureFinance acts as the Service Provider (SP)
- Users authenticate once at TechCorp and gain access to SecureFinance applications
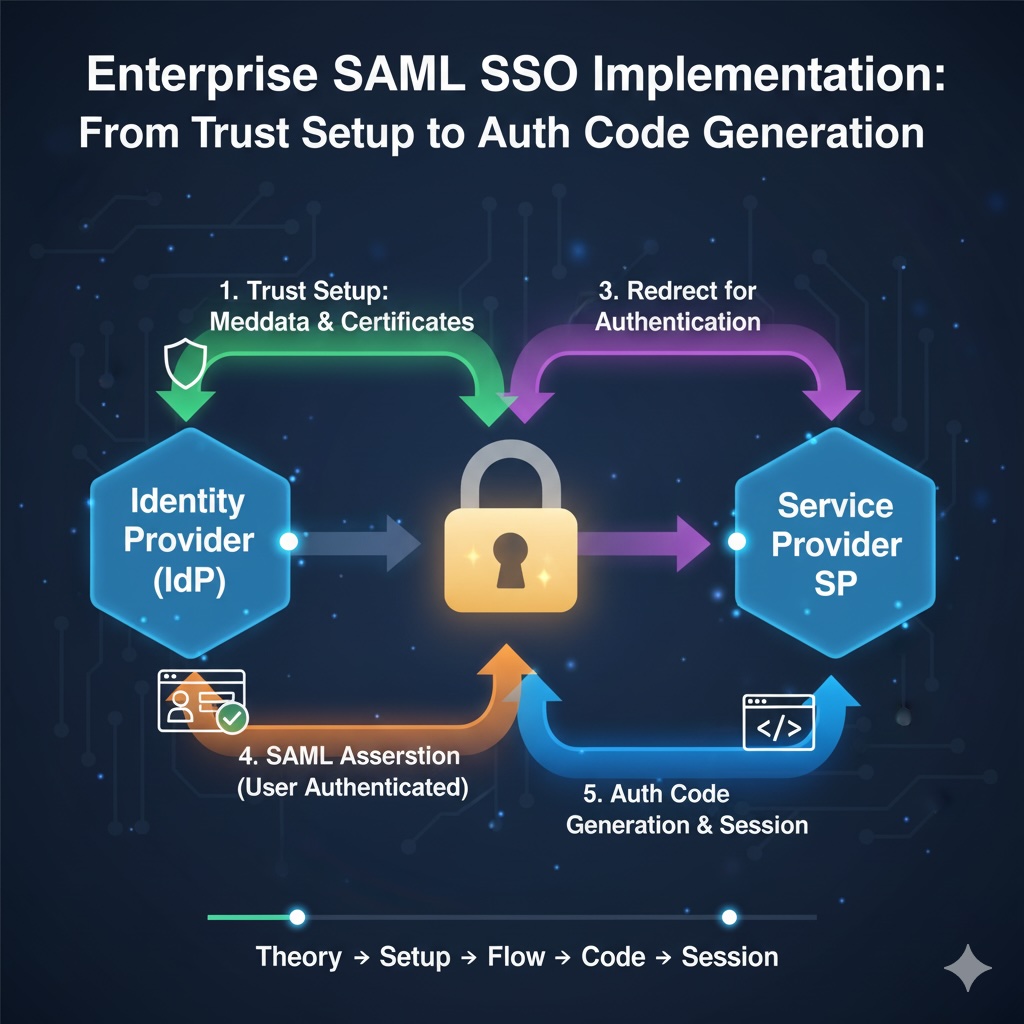
SAML SSO Architecture Overview
Core Components
TechCorp Identity Provider (IdP):
- Authenticates users (employees, customers)
- Issues SAML assertions with user attributes
- Maintains user directory and authentication policies
- Signs SAML responses for trust verification
SecureFinance Service Provider (SP):
- Receives and validates SAML assertions
- Establishes a trust relationship with TechCorp IdP
- Generates auth codes after successful SAML validation
- Hosts the Retail Banking Application
High-Level Architecture
Trust Relationship Setup
Before SAML SSO can function, a trust relationship must be established between TechCorp (IdP) and SecureFinance (SP).
IdP Configuration at TechCorp
SP Configuration at SecureFinance
SAML SSO Authentication Flow
The complete SAML SSO flow consists of several critical steps from initial access attempt to successful auth code generation.
Complete SSO Flow Sequence
Auth Code Generation Process
The auth code represents a critical security token that bridges the SSO authentication with the subsequent authorization phase.
Auth Code Characteristics
Security Properties:
- One-time use: Each auth code can only be exchanged once
- Short-lived: Expires in 10 minutes to minimize attack window
- Cryptographically secure: Generated using secure random algorithms
- Bound to session: Tied to the authenticated user session
Technical Implementation:
Auth Code Validation Rules
Role-Based User Context
The SAML assertion contains user attributes that determine the role-based context for authorization decisions.
User Role Mapping
| SAML Attribute | Role Value | Application Context |
|---|---|---|
techcorp:role | personal-banking-customer | Individual account access |
techcorp:role | business-banking-customer | Corporate account management |
techcorp:role | relationship-manager | Client advisory services |
techcorp:role | banking-operations-staff | Administrative functions |
Attribute Processing Flow
Implementation Deep Dive
SAML Configuration Details
TechCorp IdP Configuration:
<EntityDescriptor entityID="urn:techcorp:identity">
<IDPSSODescriptor>
<KeyDescriptor use="signing">
<KeyInfo>
<X509Data>
<X509Certificate>MIIBkTCB...signing cert...</X509Certificate>
</X509Data>
</KeyInfo>
</KeyDescriptor>
<SingleSignOnService
Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST"
Location="https://techcorp.com/saml/sso"/>
<Attribute Name="techcorp:role"/>
<Attribute Name="techcorp:customer-id"/>
</IDPSSODescriptor>
</EntityDescriptor>
SecureFinance SP Configuration:
<EntityDescriptor entityID="urn:securefinance:banking">
<SPSSODescriptor>
<AssertionConsumerService
Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST"
Location="https://securefinance.com/saml/acs"
index="0"/>
</SPSSODescriptor>
</EntityDescriptor>
Session Management
The auth code serves as the bridge between SAML SSO authentication and OAuth2-style token exchange:
Security Considerations
SAML Security Best Practices
Assertion Security:
- All SAML responses must be digitally signed
- Use strong certificate key lengths (2048-bit minimum)
- Implement assertion expiration timeouts
- Validate assertion conditions and audience restrictions
Transport Security:
- Enforce HTTPS for all SAML endpoints
- Use secure cookie flags for session management
- Implement CSRF protection for SAML POST bindings
Auth Code Security:
- Use cryptographically secure random generation
- Implement strict expiration policies (10 minutes max)
- Ensure one-time use enforcement
- Bind auth codes to specific sessions
Attack Prevention
Best Practices
SSO Implementation Checklist
Pre-Implementation:
- [ ] Establish certificate management procedures
- [ ] Define user attribute mapping standards
- [ ] Plan session timeout and security policies
- [ ] Design error handling and user experience flows
Implementation:
- [ ] Validate SAML metadata exchange
- [ ] Test signature validation thoroughly
- [ ] Implement proper session management
- [ ] Configure secure auth code generation
Post-Implementation:
- [ ] Monitor SAML assertion validation logs
- [ ] Track auth code usage patterns
- [ ] Implement security incident response procedures
- [ ] Regular certificate rotation schedule
Performance Optimization
Caching Strategy:
- Cache SAML metadata to reduce lookup times
- Use Redis for auth code storage with automatic expiration
- Implement connection pooling for IdP communications
Monitoring and Alerting:
- Track SAML assertion validation failures
- Monitor auth code expiration rates
- Alert on unusual authentication patterns
Conclusion
The SAML SSO implementation provides a robust foundation for secure authentication in enterprise environments. By establishing proper trust relationships between TechCorp (IdP) and SecureFinance (SP), users can seamlessly access the Retail Banking Application while maintaining strong security controls.
Key achievements of this SSO implementation:
- Seamless User Experience: Single authentication provides access to multiple applications
- Strong Security: Digital signatures and secure auth codes protect against common attacks
- Scalable Architecture: Trust-based model supports multiple service providers
- Audit Trail: Complete logging of authentication events for compliance
- Role-Based Context: User attributes flow through to enable appropriate authorization
The auth code generated at the end of this SSO flow serves as the secure handoff point to the authorization system, which will handle token exchange and API access control in the next phase of the user journey.
Next Steps: With successful SSO authentication complete and the auth code generated, the system is ready to proceed to the authorization flow, where the auth code will be exchanged for access tokens that enable secure API access to banking services.
Auto Amazon Links: No products found.
